Epilepsy is the chronic medical condition in which a child has repeated seizures. It’s also called a seizure disorder. There are many types of epilepsy, ranging from benign to intense.
In a healthy brain different groups of cells called neurons, are all firing action potentials at different times.
During a seizure, firing rates are increased and groups of neurons all fire at the same time, leading to large spikes in neural activity. This activity causes physical or behavioral changes in the body called epilepsy.
Causes of Epilepsy
- Infectious diseases (AIDS and Meningitis)
- Stroke
- Serious illness or very high fever
- Some inherited genetic factors can make a brain injury that occurs before birth. It can happen because of; Infection in the mother, Poor nutrition and Deficiency of oxygen
- Developmental disorder (Autism and Neurofibromatosis)
Symptoms of Epilepsy
The most common symptom of epilepsy is a seizure and it depends from person to person according to the type of seizure. Doctor diagnosed seizure type either it is Focal (partial) and Generalized.
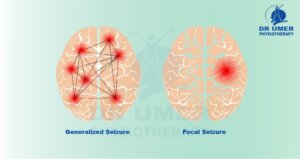
Focal (partial) seizure
Focal seizures result from abnormal activity in one part of the brain. The symptoms include;
- Dizziness
- Change and sense of taste
- Smell
- Sound
- Tingling
- Twitching of limb
- Jerking of a body part (arm or leg)
Complex focal seizure
Complex focal seizure is characterized by loss of consciousness or awareness. The symptoms include;
- Unresponsiveness to the environment
- Staring blankly into space
- Performing repetitive movements (hand rubbing, walking in circles or chewing)
Generalized seizure
The generalized seizure involves the whole brain. There are six types of generalized seizure symptoms. It includes;
Tonic seizures: causes muscle stiffness, they affect the muscles in the back neck and arm. It also leads to a fall.
Atonic seizures: causes a loss of muscle control and it may result in a sudden collapse.
Absence seizures: it often occurs in children and characterized by subtle body movement such as blinking and staring into space.
Clonic seizures: it is associated with rhythmic or repeated jerky muscle movement of the face, neck and arm.
Myoclonic seizures: causes twitches of the arm and leg.
Tonic-clonic seizures: causes stiffening of the body, shaking, loss of consciousness, loss of bladder control and biting of the tongue.
How to Diagnose Epilepsy?
Blood test helps to diagnose the epilepsy. Like;
- Glucose level
- Liver function
- Kidney function
- Infectious diseases
Brain scan is the best way to diagnose the epilepsy. Like;
- Computerized axial tomography (CT scan)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Treatment
In epilepsy, medication is the first way to treat. If the medications do not treat the condition then surgery is the next option. In between, physiotherapy helps to manage the severity of symptoms according to the condition.
Physiotherapy in epilepsy helps patients to manage their daily routine work. It helps to maintain the joint mobility and also reduces stiffness. Physiotherapy helps to strengthen the muscles and increase the range of motion.
Physiotherapist can diagnose the type of epilepsy and will arrange your treatment plan with your family or parents. Physiotherapy in epilepsy mostly needs, when the patient loss balance and cannot do his daily routine work. Physical exercises prevent you to fall. Physiotherapist guides you the exercises program according your symptoms.